What is inheritance tax in the UK?
Inheritance tax (IHT) is the tax paid on the estate of a deceased person. It’s chargeable on the value of the estate above the tax-free threshold of £325,000. At present inheritance tax is 40%.
While it certainly affects beneficiaries’ inheritance, it is not paid by the beneficiaries of the deceased’s will. Instead, it is deducted from the value of the estate by an executor before transferring the final amount to beneficiaries. It won’t surprise you to find out that it is the UK’s most unpopular tax, incurred simply by dying, rather than by some kind of gain or income as most other taxes are. It is sometimes sarcastically referred to as a death tax.
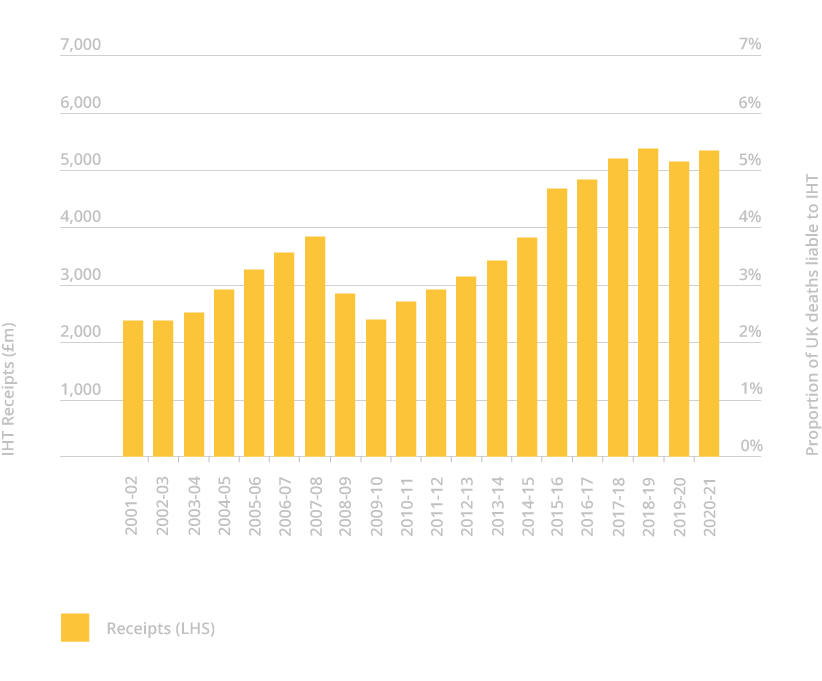
Graph showing IHT receipts from tax year 2001 to 2002 to tax year 2020 to 2021
Getting your estate planning in shape
Increasingly, with the freeze on the tax-free threshold and rising house prices, more middle-income families are getting caught by IHT. Don’t let this happen to you.
Inheritance tax planning requires careful consideration and timing. With the right actions and measures put in place – such as gifting assets seven years prior to death for them to be exempt from the tax, or making investments into schemes that offer IHT exemption – you can ensure you keep your exposure to a minimum, or reduce it to zero.
Download our free guide to inheritance tax to learn more about it and ways to mitigate or reduce it.
Get your free guide to EIS and inheritance tax

Putting EIS to work for your estate planning.
Do you know the value of your estate? The number of UK households likely to face an inheritance tax bill is increasing every year. Find out more about reducing your inheritance tax bill with business relief and EIS. You'll also discover the other tax reliefs and potential for returns available to EIS investors in our latest publication.
How does inheritance tax work?
When a person dies the value of their estate is calculated. Add up the value of their home, assets, possessions, less debts and liabilities. The estate pays tax on the amount above the threshold. Distribute the rest to the beneficiaries.
Ways to mitigate inheritance tax
There are a number of IHT reliefs and exemptions available. To start, there is no IHT if you leave everything above the threshold to your spouse, a charity, or an amateur sports club.
If you give away your home to your children, your tax-free threshold can increase to £500,000
If you leave 10% or more of your estate to charity, you can pay a reduced rate of 36% on some assets.
Investments exempt from IHT
Certain types of assets gain IHT exemption through Business Relief (BR) - formerly called Business Property Relief (BPR). BR applies to shares in unlisted companies and some listed on the Alternative Investment Market (AIM). Early-stage companies that offer EIS or SEIS tax relief also offer IHT relief. In all cases, shares are exempt from IHT provided they have been held for at least two years at the time of death.
EIS and inheritance tax relief
The Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS) and Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS) offer IHT relief. This means they are not included in the estate value calculation. Investments in EIS-eligible companies, or through funds, offer investors additional tax reliefs. These include income tax relief, capital gains tax deferral and loss relief on failed investments.
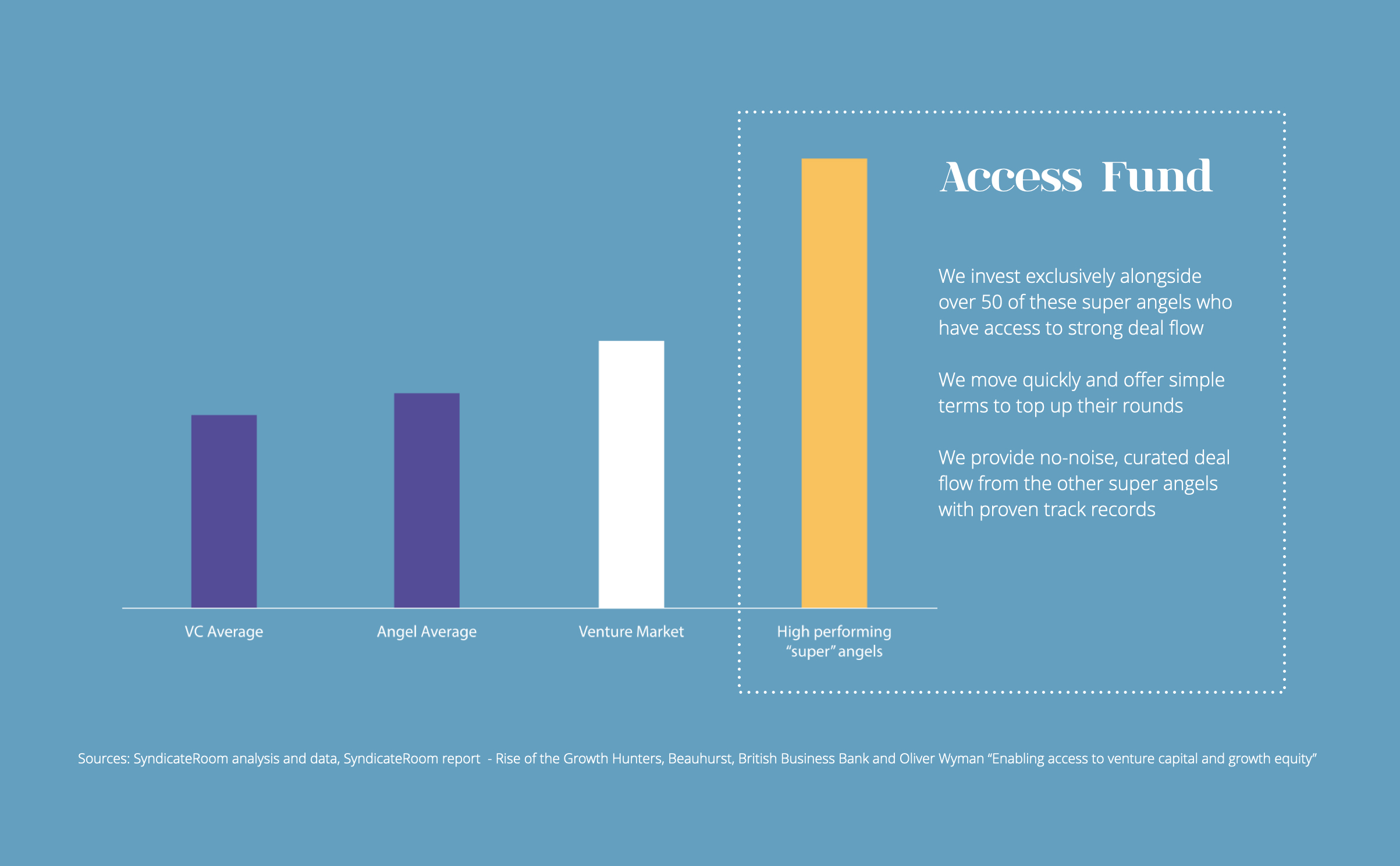
The Access EIS Fund
Our Access EIS Fund tracks the performance data of over 1,000 active startup investors. It then selects and co-invests with some of the best-performing “super angels” in the UK. The aim is to replicate their collective success. Diversifying across at least 50 super-angel-backed startups helps minimise risk. It also increases the chance of capturing as many potential “blockbusters” as possible. Our super angels significantly outperform the market.
We make the process of claiming relief on multiple investments as simple as possible for our investors. If you are thinking about EIS and IHT we would welcome the chance to speak.
Find out more about the fund and the innovative startups we've backed here. If it’s right for you, we'd love to welcome you into our community of more than 500 investors.
Inheritance tax threshold and rules
Alongside EIS and SEIS, investors often look at Venture Capital Trusts, or VCTs, for tax-efficient investing. However, VCTs do not offer IHT relief. When you buy shares in a VCT, you are buying shares in the trust itself, not in its holdings. With EIS and SEIS, you buy shares in the companies themselves, even if you invest through a fund.
How much is inheritance tax?
Inheritance tax stands at 40%. The estate pays iht on the amount above the threshold. Leaving a large portion of one's estate to charity may reduce this rate.
What is the inheritance tax threshold?
At the time of writing this, and until 2028, the threshold is £325,000. This stays fixed until 2028.
When do you pay inheritance tax?
HMRC requires payment by the end of the sixth month after the person's death. The executor of the will ensures payment of the tax using funds from the estate.
What is the 7-year rule?
The seven-year rule refers to no tax being due on any gifts you give if you live for 7 years after giving them - unless the gift is part of a trust.
What is the Nil Rate Band (NRB), and what are the rules around married couples?
The Nil Rate Band (NRB) is the value of an estate that does not incur inheritance tax. At present, the NRB stands at £325,000. Surviving partners can transfer unused NRB from their deceased partner/spouse to themselves. In doing so the max NRB doubles to £650,000.
How does IHT work for residential property, and how does the Residence Nil Rate Band (RNRB) work?
A home left to a spouse or civil partner does not incur IHT. If left to a person's children or grandchildren, it adds an RNRB value to the existing NRB value. The RNRB stands at $175,000 (until 2026). Leaving a home to one's children raises the NRB from £325,000 to £500,000 per individual. So for couples, this would be £1,000,000.
Disclaimer.
The information on this page does not constitute financial advice and is provided on an information basis only, based on research using the following sources: